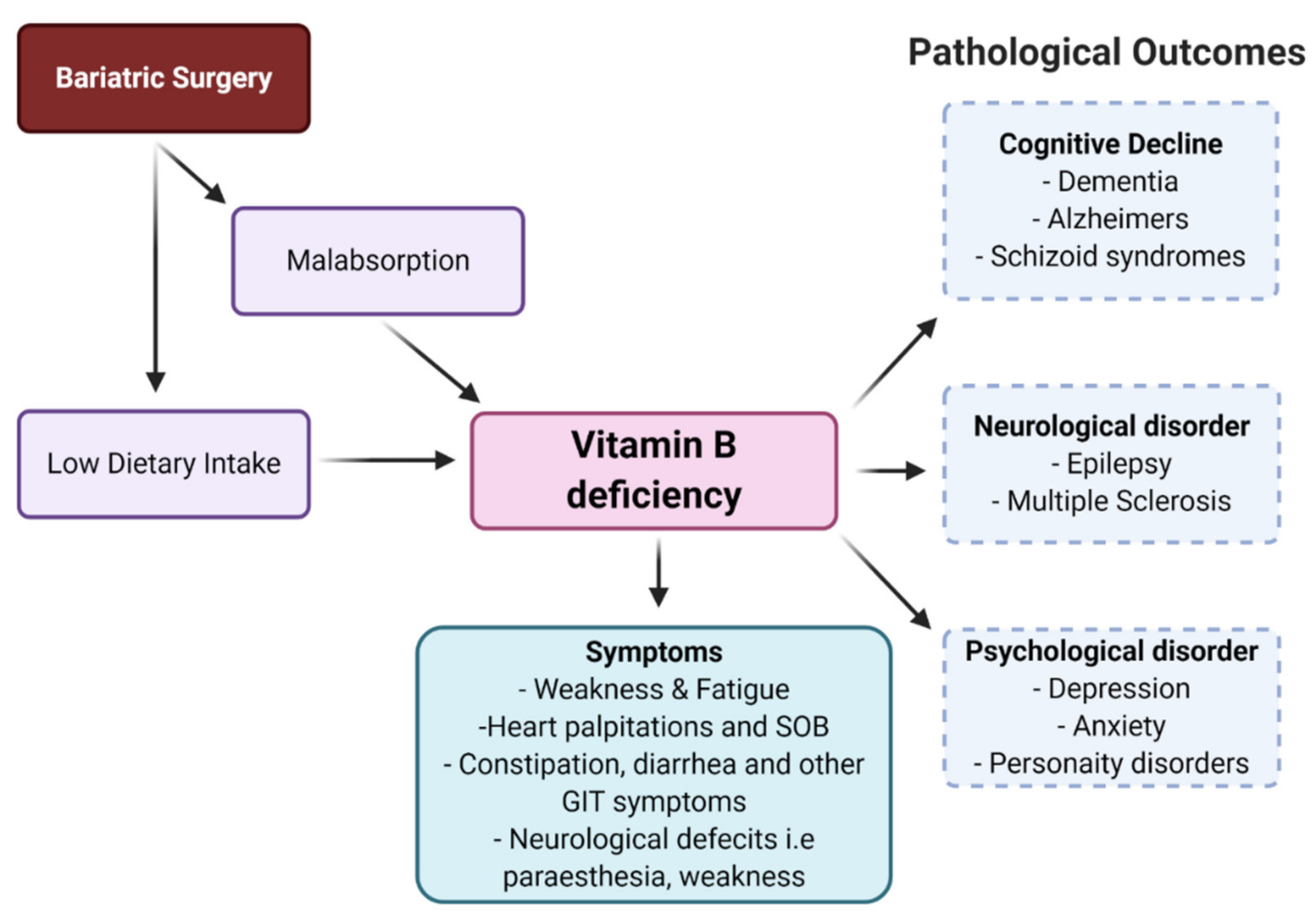
The Unspoken Side Effect: Is Ozempic Affecting Your Mental Health?
You might notice that Ozempic helps with weight loss but could also subtly impact your mental health. Changes in mood, increased anxiety, or emotional numbness are common yet often overlooked side effects. These effects stem from how the medication influences brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine. Recognizing these emotional shifts is important for your overall well-being. Exploring these connections further can provide insights into managing both physical and mental health effectively.
Understanding Ozempic and Its Popularity
Have you ever wondered why Ozempic has become so widely popular? Its rapid effectiveness in promoting weight loss appeals to many, but understanding its popularity requires deeper insight into its psychological impact. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, Ozempic influences not just physical health but also emotional well-being. Users often report improved confidence and reduced anxiety related to weight concerns, which contribute to enhanced psychological stability. However, the mechanism behind this success also underscores the importance of recognizing potential mental health changes. The emotional well-being of individuals using Ozempic can be profoundly affected by both positive and negative experiences, shaping their overall perception of health and self-esteem. Its popularity isn’t solely driven by clinical outcomes but also by the hope it offers for emotional resilience. Mastery over understanding this connection equips you to better navigate the complex interplay between physical treatment and psychological health, fostering a more holistic approach to well-being.
The Connection Between Weight Loss Medications and Mental Health
Weight loss medications like Ozempic can considerably influence mental health, not just through physical changes but also by affecting emotional states and self-perception. These drugs may alter dopamine regulation, impacting how you experience pleasure and motivation, which are essential for emotional resilience. As your body adapts to medication, shifts in mood, motivation, or anxiety levels can occur, sometimes unexpectedly. This connection underscores the importance of understanding that weight loss isn’t solely a physical journey; it intertwines deeply with mental well-being. You might find that improvements in body image boost confidence, but fluctuations in emotional resilience can also arise, highlighting the complex relationship between these medications and mental health. Recognizing these effects enables you to better navigate your experience, advocate for your emotional needs, and seek appropriate support. Ultimately, understanding this connection helps you master both physical health and emotional stability on your weight loss journey.
Personal Stories: How Some Users Are Affected Emotionally
Many users of Ozempic report that their emotional experiences while on the medication are complex and varied. Personal experiences reveal a range of emotional reactions, from heightened mood swings to feelings of emotional numbness. Some individuals notice increased anxiety or irritability, while others describe a surprising sense of emotional flatness or detachment. These reactions can be subtle or pronounced, often fluctuating with dosage changes or personal circumstances. Recognizing these patterns is vital, as they highlight how medication can influence mental states beyond physical effects. Your personal stories underscore the importance of validating emotional responses during treatment, acknowledging that such changes are real and deserving of attention. While some may feel these experiences are isolated, collective reports suggest a nuanced relationship between Ozempic and emotional well-being. Understanding these personal impacts is essential for developing a thorough approach to managing both physical and mental health during therapy.
Scientific Insights Into Ozempic’s Impact on Mood and Anxiety
Scientific research indicates that GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic can influence neural pathways involved in mood regulation and anxiety. These medications may alter neurotransmitter balance, affecting serotonin, dopamine, and other neurochemicals vital for emotional stability. Additionally, Ozempic’s impact on hormonal regulation extends beyond blood sugar control, potentially affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which governs stress responses. Such changes can subtly influence mood states, leading to feelings of anxiety or emotional shifts in some individuals. While these effects are not universal, understanding the neurobiological mechanisms helps clarify why some users experience mental health alterations. The evidence suggests that Ozempic’s influence on neural circuits involved in emotional processing warrants careful consideration, especially for those with pre-existing mood or anxiety disorders. Recognizing these scientific insights empowers you to better monitor your mental health and seek appropriate support when needed.
Potential Mechanisms Behind Emotional Side Effects
Understanding how Ozempic may cause emotional side effects involves examining its influence on neural and hormonal systems. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, Ozempic can lead to neurotransmitter disruption, affecting mood regulation pathways. Altered levels of serotonin, dopamine, or norepinephrine may contribute to feelings of depression, anxiety, or emotional instability. Additionally, hormonal imbalance caused by Ozempic’s impact on insulin and glucagon signaling can influence brain chemistry and stress responses. These hormonal shifts may amplify emotional fluctuations, especially in individuals with preexisting mental health vulnerabilities. The intricate interplay between neurotransmitter activity and hormonal regulation underscores how metabolic interventions can inadvertently affect mental well-being. Recognizing these mechanisms offers insight into why emotional side effects occur and emphasizes the importance of monitoring mental health during treatment. A nuanced understanding of these processes can empower you to seek appropriate support and engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers.
Weighing the Benefits Against Possible Mental Health Risks
While Ozempic offers significant benefits for weight management and blood sugar control, it’s essential to carefully consider the potential mental health risks associated with its use. You must evaluate whether the improvements in physical health outweigh possible impacts on emotional resilience, especially if you experience mood fluctuations or anxiety. Recognize that mental health stigma can hinder open discussions about these side effects, making it harder to seek support. Developing awareness of your emotional responses helps you gauge if Ozempic affects your mental well-being. Weighing these factors involves honest reflection on how your mental health evolves alongside physical benefits. It’s vital to remember that prioritizing mental resilience isn’t a sign of weakness but a necessary step toward comprehensive health mastery. Ultimately, making informed decisions requires balancing the tangible benefits of medication with the subtle, yet profound, effects on your mental state.